PUBLICATIONS
PATENTS
PLACED TRAINEES
HACKATHON WINS

The purpose of speech, braille and sign are communication, and the research in these areas primarily deals with processing, representation of speech signal, recognization of typed braille or presented sign that leads to the development of voice, braille and sign based interfaces for man-machine interaction. Such natural interfaces enable access to information via hands-free mode, to literate, illiterate as well as divyagjan people. The thrust of our activity in Speech and Multimodal Laboratory is on the development of speech, braille and sign based interfaces for man-machine interaction. The objective of Speech and Multimodal Laboratory is to conduct goal-oriented basic research, and thus we address fundamental issues involved in building robust speech-to-text systems, text to sign generation and text to braille generation applications.

PhD Scholar
Expertise in Speech Processing, Augmentation Techniques, Text Processing, Software Planning and Execution
Email - : puneet.bawa@chitkara.edu.in

Assistant Professor-Selection Grade, Department of Computer Science
UPES-Dehradun

Junior Research Fellow at Chitkara University in collaboration with Defense Research & Development Organization (DRDO)

Skills: AI/ML, Automation, Linguistics, Back-End Development

Skills: Linguistics, Research Analyst, Back-End Development, Content Write

Placed (Stryker, Gurgaon

Placed (LIDO, Noida)
Placed (Sears Holdings,Pune)

Placed (Nagarro, Gurgaon)

Placed (JTG, Gurgaon)

Placed (Gojek,Mumbai)

Placed( HCIA, Bengaluru

Placed(FICO,Bengaluru)

Placed (Privafy, Bengaluru

To be updated...

Placed (Gemini Solutions Pvt Ltd, Panchkula

Board Member and AI/ML Engineer at Sellebration

Placed ( Idea Clan, Panchkula)

Full Stack Developer Freelance
CURIN AI Faculties Attended RPA Workshop At NITTTR Chandigarh From 22-26 July 2019.CURIN faculty members Dr Luxmi Dapra, Dr Nitin Goyal and Dr Virender Kadyan of the M Tech (AI) course attended the week long training at NITTTR, Chandigarh on Robotic Process Automation being conducted by UiPath. |
 |
|---|---|
Dr. Virender Kadyan Conducted Speech Recognition Using Machine Learning Steam School Workshop From 18-22 Feb 2019Dr Virender Kadyan Assistant Professor-Research and his team members Ms Sashi Bala, Mr Puneet Bawa and Mr Rishab researchers of Speech & Multimodal Laboratory has conducted the Batch-II of Steam School 2019 workshop on Speech Recognition using Machine learning from 18-22 Feb 2019. Dr Kadyan gave an introductory session on Machine learning approaches in aspects of recognition of uttered words. Day 2 has been designed so that students can perform Hands on sessions on Speech to text recognition systems. On day3 students learnt about the formation of Chat Bots and also tried to embed it with uttered speech signals. Finally students build their own Chat Bots on Day4 and day5 with sample text corpus in Hindi or English languages. |
 |
Dr Virender Kadyan Organised 10 Days Research Induced Training-V From 18 Dec To 29 Dec 2018Dr Virender Kadyan Assistant Professor CURIN has organised 10 Days Research Induced Training-V from 18 Dec to 29 Dec 2018o. The training involved four modules for BE/BCA students of Chitkara University. Valedictory of the event is graced with presence of Chief Guest Dr Archana Mantri Pro-VC CURIN and Dr S N Panda Director Research along with faculty members. |
 |
Dr Virender Kadyan Assistant Professor Has Conducted The Day 2 Of Introduction To Linux Steam School 2018Dr Virender Kadyan Assistant Professor CURIN has conducted the day2 of Introduction to Linux Steam School 2018. He has taught the basics of shell scripts. Students have performed hands-on practice on their Linux machines with some scenario based examples. |
 |
Summer School On Research Trends In Network Security, Machine And Deep Learning, Image And Multimedia Processing, June 201810 days summer school is successfully organized on Research Trends in Network Security, Machine and Deep Learning, Image and Multimedia Processing by Dr K R Ramkumar in support with Dr Shefali Dr Deepika Kaundal Dr Virender kadyan and Er Sarvesh CURIN. Participants gain knowledge on interdisciplinary areas of different research domains. Participants learned the art of writing a research paper. Around 52 research papers are generated as an outcome of the workshop. |
 |
Techno SoundsTechno Sounds 2016 Ist and IInd round were held on 13 October 2016 and 10 November 2016 at Speech and Multimodal Laboratory in association with CSI student Chapter at Chitkara University, Punjab.Er. Virender Kadyan, Assistant Professor, shared in brief about Techno Sounds 2016 and provide opportunity to students to show case their innovative ideas. A total of 24 teams registered for the event in the Ist round, out of which 9 teams got selected for second round to represent the prototype of their ideas. Mr. Vinay Kukreja, Assistant Professor , CSE department and Mr. Jaswinder Singh, Assistant Professor, CA department judged the event. The event was succesfully managed by Ms. Kanika and event coordinators. Further, shortlisted teams were qualified for the IIIrd round held on 24 January 2017, in which students had to showcase their complete product. |


|
Summer SchoolChitkara University Research and Innovation Network (CURIN) had organised a Summer School from June 20, 2016 to July 2, 2016. This Summer School included 16 workshops in most relevant topics of research and academics ranging from Computer Science, Electronics and Communication to Mechanical Engineering. These workshops were specially designed to cater the need of state of the art research and development in forefront areas. The main goal of the Summer School was to provide knowledge to students, research scholars and academicians to start research and development in pioneer research areas. |
 |
ASR using Word Based Modeling, 18 March, 2016Dr. Amitoj Singh (Assistant Director-Research) and Er. Virender Kadyan (Assistant Professor-Research) organized one day workshop on Hindi ‘ASR using Word Based Modeling’ at CU, Himachal campus. The audiences for this workshop included the students of CSE/ECE department. This workshop threw light on practical feasibility of making ASR for own language. Dr Amitoj began his talk by giving an introduction to Language Processing and its importance in a researcher’s life. The focus was on how to select and process a particular language. He then explained present state of availability of ASR system in Indian Language. In another session, Er Virender, gave a hands-on experience on How to recognize a particular word in Hindi language using HTK toolkit. He addressed the use of various acoustic modeling technique to process a small vocabulary Hindi ASR system |
|
Automatic Speech Recognition , 9-10th Oct, 2015Dr. Amitoj Singh, Assistant Director, Mr. Virender Kadyan, Assistant Professor and Mr. Vinay Kukreja, Assistant Professor, CURIN, CU, Punjab conducted a two-day workshop on “Automatic Speech Recognition” under ACM Student Chapter. Guest speakers enriched the workshop with their knowledge and skills and imparted practical sessions to engross students for inter-relating theoretical skills with practical implementation. Dr. Sumapreet Kaur from Punjabi University, Patiala gave an introduction on Phonology and Linguistics. Mrs. Rupinder Kaur from Thapar University, Patiala encouraged a hands-on session for building ASR system using HTK. Dr. Wiqas Ghai imparted hands-on session on Phone Based Modelling using HTK. The workshop emphasized an active participation of students as well as faculty members from within and outside University. |


|
Abstract: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a severe disorder in which brain cells degenerate, increasing memory loss with treatment choices for AD symptoms varying based on the disease's stage, and as the disease progresses, individuals at certain phases undergo specific healthcare. The majority of existing studies make predictions based on a single data modality either they utilize magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/positron emission tomography (PET)/diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) or the combination of these modalities. However, a thorough understanding of AD staging assessment can be achieved by integrating these data modalities and performance could be further enhanced using a combination of two or more modalities. However, deep learning techniques trained the network from scratch, which has the following drawbacks: (a) demands an enormous quantity of labeled training dataset that could be a problem for the medical field where physicians annotate the data, further it could be very expensive, (b) requires a huge amount of computational resources. (c) These models also require tedious and careful adjustments of numerous hyper-parameters, which results to under or overfitting and, in turn, to degraded performance. (d) With a limited medical training data set, the cost function might get stuck in a local-minima problem. In this chapter, a study is done based on the models used for AD diagnosis. Many researchers fine-tuned their networks instead of scratch training and utilized CaffeNet, GoogleNet, VGGNet-16, VGGNet-19, DenseNet with varying depths, Inception-V4, AlexNet, ResNet-18, ResNet-152, or even ensemble transfer-learning models pretrained on generalized images for AD classification performed better
Abstract:Development of a native language robust ASR framework is very challenging as well as an active area of research. Although an urge for investigation of effective front-end as well as back-end approaches are required for tackling environment differences, large training complexity and inter-speaker variability in achieving success of a recognition system. In this paper, four front-end approaches: mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), Gammatone frequency cepstral coefficients (GFCC), relative spectral-perceptual linear prediction (RASTA-PLP) and power-normalized cepstral coefficients (PNCC) have been investigated to generate unique and robust feature vectors at different SNR values. Furthermore, to handle the large training data complexity, parameter optimization has been performed with sequence-discriminative training techniques: maximum mutual information (MMI), minimum phone error (MPE), boosted-MMI (bMMI), and state-level minimum Bayes risk (sMBR). It has been demonstrated by selection of an optimal value of parameters using lattice generation, and adjustments of learning rates. In proposed framework, four different systems have been tested by analyzing various feature extraction approaches (with or without speaker normalization through Vocal Tract Length Normalization (VTLN) approach in test set) and classification strategy on with or without artificial extension of train dataset. To compare each system performance, true matched (adult train and test—S1, child train and test—S2) and mismatched (adult train and child test—S3, adult + child train and child test—S4) systems on large adult and very small Punjabi clean speech corpus have been demonstrated. Consequently, gender-based in-domain data augmented is used to moderate acoustic and phonetic variations throughout adult and children’s speech under mismatched conditions. The experiment result shows that an effective framework developed on PNCC + VTLN front-end approach using TDNN-sMBR-based model through parameter optimization technique yields a relative improvement (RI) of 40.18%, 47.51%, and 49.87% in matched, mismatched and gender-based in-domain augmented system under typical clean and noisy conditions, respectively.
Abstract:
Objective: To propose a theoretical formulation of engeletin-nanostructured lipid nanocarriers for improved delivery and increased bioavailability in treating Huntington’s disease (HD).
Methods: We conducted a literature review of the pathophysiology of HD and the limitations of currently available medications. We also reviewed the potential therapeutic benefits of engeletin, a flavanol glycoside, in treating HD through the Keap1/nrf2 pathway. We then proposed a theoretical formulation of engeletin-nanostructured lipid nanocarriers for improved delivery across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and increased bioavailability.
Results: HD is an autosomal dominant neurological illness caused by a repetition of the cytosine-adenine-guanine trinucleotide, producing a mutant protein called Huntingtin, which degenerates the brain’s motor and cognitive functions. Excitotoxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, elevated concentration of ROS and RNS, neuroinflammation, and protein aggregation significantly impact HD development. Current therapeutic medications can postpone HD symptoms but have long-term adverse effects when used regularly. Herbal medications such as engeletin have drawn attention due to their minimal side effects. Engeletin has been shown to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction and suppress inflammation through the Keap1/NRF2 pathway. However, its limited solubility and permeability hinder it from reaching the target site. A theoretical formulation of engeletin-nanostructured lipid nanocarriers may allow for free transit over the BBB due to offering a similar composition to the natural lipids present in the body a lipid solubility and increase bioavailability, potentially leading to a cure or prevention of HD.
Conclusion: The theoretical formulation of engeletin-nanostructured lipid nanocarriers has the potential to improve delivery and increase the bioavailability of engeletin in the treatment of HD, which may lead to a cure or prevention of this fatal illness.
Abstract:The development of numerous frameworks and pedagogical practices has significantly improved the performance of deep learning-based speech recognition systems in recent years. The task of developing automatic speech recognition (ASR) in indigenous languages becomes enormously complex due to the wide range of auditory and linguistic components due to a lack of speech and text data, which has a significant impact on the ASR system's performance. The main purpose of the research is to effectively use in-domain data augmentation methods and techniques to resolve the challenges of data scarcity, resulting in an increased neural network consistency. This research further goes into more detail about how to create synthetic datasets via pooled augmentation methodologies in conjunction with transfer learning techniques, primarily spectrogram augmentation. Initially, the richness of the signal has been improved through the process of deformation of the time and/or the frequency axis. The time-warping aims to deform the signal's envelope, whereas frequency-warping alters spectral content. Second, the raw signal is examined using audio-level speech perturbation methods such as speed and vocal tract length perturbation. These methods are shown to be effective in addressing the issue of data scarcity while having a low implementation cost, making them simple to implement. Nevertheless, these methods have the effect of effectively increasing the dataset size because multiple versions of a single input are fed into the network during training, likely to result in overfitting. Consequently, an effort has been made to solve the problem of data overfitting by integrating two-level augmentation procedures via pooling of prosody/spectrogram modified and original speech signals using transfer learning techniques. Finally, the adult ASR system was experimented on using deep neural network (DNN) with concatenated feature analysis employing Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), pitch features, and the normalization technique of Vocal Tract Length Normalization (VTLN) on pooled Punjabi datasets, yielding a relative improvement of 41.16 percent in comparison with the baseline system.
Abstract:The usage of Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) in educational contexts has grown as a result of measurements of the speech signal in the claimed identity's native tongue. Even though resource-rich languages have received a lot of attention, low-resource languages, like Punjabi, still require work to be done on the development of ASV systems. In this study, an effort has been put forth to create an ASV system based on an i-vector for children while authenticating the student's dialects in Punjab region. Additionally, it has been determined how changing the Universal Background Model (UBM) size and i-vector dimensionality for the proposed system would affect the performance measure i.e. Equal Error Rate (EER). Finally, the EER values for the Malwa and Majha regions were lower than expected, at 8.47% and 9.26%, respectively. However, the output shows a large EER of 14.25% in Doaba region in comparison to that of Malwa and Majha regions.
Abstract: Covid-19 pandemic is of major concern that largely impacts the human and growth of respective countries. Countries like India also tried their best to manage this Covid outbreak situation through lockdown and handle its growth through strict relaxation using zonal distribution strategy. An urge of proper estimation for this outbreak is required, which can be beneficial in arrangement of proper healthcare facilities in different states of the country. India has wide diversity between its states. The effect of temperature and dense population have been two key parameters that have been poorly studied with respect to each state. In this paper, we tried to forecast the number of Covid-19 cases (8 Jan 2020 to 25 April 2020) using Kalman filter at state and national levels to generate various trends and patterns. Our analysis has been evaluated on four classification of states: most affected, moderate affected, least affected and pandemic free states. The results have been collected on vulnerable temperature parameters (historical and forecast data) of each state. The national level estimates are further compared with other countries like United States of America, Spain, France, Italy and Germany through confirmed, recovered and death cases. In the current lockdown situation our estimation shows that India should expect as many as 60,140 cases by May 24, 2020. The trends achieved shows that India has been found to be one of the beneficiaries of lockdown decisions but failed at some places in its regions due to social activities, huge dense population and temperature variation. This study will be beneficial for different state level bodies to manage various health care resources between its states or can support intra-state and can start their administrative functionality accordingly.
Abstract: The development of speech-based real-time framework for different fields and applications with the use of machine learning has indeed become a routine trend. In the past few decades, researchers have focused on integrating ensemble learning methods alongside the use of semi-supervised learning paradigm to construct more detailed and efficient classification systems. Likewise, male and female anatomical differences in human speech are related to the variation in thickness of the vocal fold or length of the vocal tract. In contrast with vocal tracts of women, vocal tracts of men are usually longer. In this chapter, investigation for developing gender classification system through the potential as well as optimal selection of the acoustic features corresponding to audio signal has been made. Moreover, this article gives readers an analysis of the complexities of speech interactions in the presence of loud backgrounds as well as their evaluations and possible impacts on practical efficiency. Finally, three semi-supervised classification algorithms including random forest, support vector machine (SVM), and multi- layer perceptron (MLP) have been experimented resulting in the increased performance of the classification system. Our preliminary experimental trials have resulted in precise gender classification effectiveness under the degraded conditions with an overall relative improvement (RI) of 8.21% leading to the development of robust and reliable predictive model.
Abstract: The manufacturing sector got revamped with the introduction of 3D printing technology. Additive manufacturing is in great demand because the products made by this technology require minimal post-processing, that too in the case of applications requiring high finishing. 3D printing is capable of producing complex shapes, as the technology uses layer by layer processing. Initially, the technology was developed to make the physical prototypes rapidly for an approximation of the real product, but now the real products are made using various 3D printing techniques which are classified according to the powder, solid, and liquid-based forms. The recent outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, from the Hubei province of China, has challenged the pharmaceutical and related medical industries with the need arising for the various medical equipment and gadgets protecting the spread of the virus. Researchers from around the world suggested various solutions for tackling the problem, introducing new products that required instant manufacturing. 3D printing is a reliable technology that succored many research groups and industries to develop and produce the products which were proved to be vital in these hard times. The chapter talks about the various success stories of the researchers who fabricated various products using 3D printing technology to tackle the complications of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Abstract: For building a successful automatic speech recognition (ASR) engine large training data is required. It increases training complexity and become impossible for less resource language like Punjabi which have zero children corpus. Consequently, the issue of data scarcity, and small vocal length of children speakers also degrades the system performance under limited data conditions. Unfortunately, Punjabi is a tonal language and building an optimized ASR for such a language is near impossible. In this paper, we have explored fused feature extraction approach to handle large training complexity using mel frequency-gammatone frequency cepstral coefficient (MF-GFCC) technique through feature warping method. The efforts have been made to develop children’s ASR engine using data augmentation on limited data scenarios. For that purpose, we have studied in-domain data augmentation that artificially combined noisy and clean corpus to overcome the issue of data scarcity in train set. The combined dataset is processed with a fused feature extraction approach. Apart, the tonal characteristics and child vocal length issues are also overcome by inducing pitch features and train normalization strategy using vocal tract length normalization (VTLN) approach. In addition to that, combined augmented and original speech signals are noted to reduce the Word error rate (WER) performance with larger relative improvement (RI) of 20.59% on noisy and 19.39% on clean environment conditions using hybrid MF-GFCC approach than that on conventional Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) and Gammatone Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (GFCC) based ASR systems
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most important causes of mortality in elderly people, and it is often challenging to use traditional manual procedures when diagnosing a disease in the early stages. The successful implementation of machine learning (ML) techniques has also shown their effectiveness and its reliability as one of the better options for an early diagnosis of AD. But the heterogeneous dimensions and composition of the disease data have undoubtedly made diagnostics more difficult, needing a sufficient model choice to overcome the difficulty. Therefore, in this paper, four different 2D and 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) frameworks based on Bayesian search optimization are proposed to develop an optimized deep learning model to predict the early onset of AD binary and ternary classification on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Moreover, certain hyperparameters such as learning rate, optimizers, and hidden units are to be set and adjusted for the performance boosting of the deep learning model. Bayesian optimization enables to leverage advantage throughout the experiments: A persistent hyperparameter space testing provides not only the output but also about the nearest conclusions. In this way, the series of experiments needed to explore space can be substantially reduced. Finally, alongside the use of Bayesian approaches, long short-term memory (LSTM) through the process of augmentation has resulted in finding the better settings of the model that too in less iterations with an relative improvement (RI) of 7.03%, 12.19%, 10.80%, and 11.99% over the four systems optimized with manual hyperparameters tuning such that hyperparameters that look more appealing from past data as well as the conventional techniques of manual selection.
Abstract: Success of any commercial Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system depends upon availability of its training data. Although, it's performance gets degraded due to absence of enough signal processing characteristics in less resource language corpora. Development of Punjabi Children speech system is one such challenge where zero resource conditions and variabilities in children speech occurs due to speaking speed and vocal tract length than that of adult speech. In this paper, efforts have been made to build Punjabi Children ASR system under mismatched conditions using noise robust approaches like Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) or Gammatone Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (GFCC). Consequently, acoustic and phonetic variations among adult and children speech are handled using gender based in-domain training data augmentation and later acoustic variability among speakers in training and testing sets are normalised using Vocal Tract Length Normalization (VTLN). We demonstrate that inclusion of pitch features with test normalized children dataset has significantly enhanced system performance over different environment conditions i.e clean or noisy. The experimental results show a relative improvement of 30.94% using adult female voice pooled with limited children speech over adult male corpus on noise based training data augmentation respectively.
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a long-term condition that causes brain areas such as memory, recognition, judgment, and speech to deteriorate. Classification of AD using neuroimaging data like MRI using artificial intelligence has become a focus of current research. Likewise, deep learning recent breakthrough in computer vision has accelerated similar research. However, fundamental shortcomings of such algorithms include their dependency on a wide range of training datasets and the need for rigorous optimization of neural network architecture. In this paper, the deep learning approach 2D-Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) has been employed to analyse architectural significance in boosting the diagnosis accuracy of different classes of images-mild, very mild, moderate, and non-demented concerning AD with parameter optimization on neuroimaging dataset. Finally, the classification accuracy using the 2D-CNN architecture considering the impact of parameters such as dense units, dropout rate, and optimizers has led to 6.83% of Relative Improvement (RI) in contrast to the base model being developed.
Abstract:Processing of low resource pre and post acoustic signals always faced the challenge of data scarcity in its training module. It’s difficult to obtain high system accuracy with limited corpora in train set which results into extraction of large discriminative feature vector. These vectors information are distorted due to acoustic mismatch occurs because of real environment and inter speaker variations. In this paper, context independent information of an input speech signal is pre-processed using bottleneck features and later in modeling phase Tandem-NN model has been employ to enhance system accuracy. Later to fulfill the requirement of train data issues, in-domain training augmentation is perform using fusion of original clean and artificially created modified train noisy data and to further boost this training data, tempo modification of input speech signal is perform with maintenance of its spectral envelope and pitch in corresponding input audio signal. Experimental result shows that a relative improvement of 13.53% is achieved in clean and 32.43% in noisy conditions with Tandem-NN system in comparison to that of baseline system respectively.
Abstract:Since the development of the additive manufacturing (AM) process also prominently known as 3D printing or rapid prototyping there is an exponential increase in its applications under various domains. 3D printing when incorporated with supply chain management can be really helpful to streamline the processes along with waste management. Various factors can be kept in mind while implementing 3D printing along with supply chain management. The waste that is generated from different manufacturing processes when they were being turned into final products can also be reduced to a great extent or can be eliminated if production is done by 3D printing. Rapid Prototyping (RP) is a layer-by-layer manufacturing process. Likewise, Computer-assisted design (CAD) can specifically be used to produce such tri-dimensional physical models. This manufacturing method gives engineers and designers an absolute ability to print the tri-dimensions layout of their concepts and models. Processes for RP includes a quick and cheap alternative for prototyping functional models in contrast with the traditional component production. The benefit of constructing a component layer-by-layer is that even the complex shapes can be easily made which though were the almost impossible to manufacture by machining process. RP can construct complex structures within structures, internal sections, and very thin-walled features equally quickly to construct a simple cube. AM technology emerges as an easy sell in the market to create complex shapes with the material needed and to enhance the design and simulation of complex structures. This results in disruption of technologies that have a global impact on the supply chain and the logistics of the business. The essence of this technology is the potential to deliver goods closer to client standards worldwide while maintaining the automated delivery of those products in real-time. It has major advantages over the management of the supply chain by reducing product, transport, and warehouse capital investment, and by encouraging stores to evaluate a global change in supply chain management. The primary goal is to acquire knowledge about the use and role of 3D printers in the management of the supply chain and to explore the consequences of AM for the management of the supply chain. The key goal of the research is to gain information on the use and role of 3D printing in supply chain management and to study AM’s effect on supply chain administration.
Abstract:The development of speech-based real-time framework for different fields and applications with the use of machine learning has indeed become a routine trend. In the past few decades, researchers have focused on integrating ensemble learning methods alongside the use of semi-supervised learning paradigm to construct more detailed and efficient classification systems. Likewise, male and female anatomical differences in human speech are related to the variation in thickness of the vocal fold or length of the vocal tract. In contrast with vocal tracts of women, vocal tracts of men are usually longer. In this chapter, investigation for developing gender classification system through the potential as well as optimal selection of the acoustic features corresponding to audio signal has been made. Moreover, this article gives readers an analysis of the complexities of speech interactions in the presence of loud backgrounds as well as their evaluations and possible impacts on practical efficiency. Finally, three semi-supervised classification algorithms including random forest, support vector machine (SVM), and multi- layer perceptron (MLP) have been experimented resulting in the increased performance of the classification system. Our preliminary experimental trials have resulted in precise gender classification effectiveness under the degraded conditions with an overall relative improvement (RI) of 8.21% leading to the development of robust and reliable predictive model.
Abstract:In real-life applications, noise originating from different sound sources modifies the characteristics of an input signal which affects the development of an enhanced ASR system. This contamination degrades the quality and comprehension of speech variables while impacting the performance of human-machine communication systems. This paper aims to minimise noise challenges by using a robust feature extraction methodology through introduction of an optimised filtering technique. Initially, the evaluations for enhancing input signals are constructed by using state transformation matrix and minimising a mean square error based upon the linear time variance techniques of Kalman and Adaptive Wiener Filtering. Consequently, Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), Linear Predictive Cepstral Coefficient (LPCC), RelAtive SpecTrAl-Perceptual Linear Prediction (RASTA-PLP) and Gammatone Frequency cepstral coefficient (GFCC) based feature extraction methods have been synthesised with their comparable efficiency in order to derive the adequate characteristics of a signal. It also handle the large-scale training complexities lies among the training and testing dataset. Consequently, the acoustic mismatch and linguistic complexity of large-scale variations lies within small set of speakers have been handle by utilising the Vocal Tract Length Normalization (VTLN) based warping of the test utterances. Furthermore, the spectral warping approach has been used by time reversing the samples inside a frame and passing them into the filter network corresponding to each frame. Finally, the overall Relative Improvement (RI) of 16.13% on 5-way perturbed spectral warped based noise augmented dataset through Wiener Filtering in comparison to other systems respectively.
Abstract:Children are likely to have trouble pronouncing vowels in real-life conversations. Therefore, it becomes necessary to handle the correct pronunciation corresponding to every vowel for the improved efficiency of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system. In this research, the linguistic study of native speakers and their auditory inconsistency was pursued using the extraction of efficient front-end speech vectors utilizing three varying fractal dimensions (FD) : Higuchi FD, Katz FD, and Petrosian FD. These depicted fractal measurements are based on precise evaluation of FD, which serves as a key parameter of fractal geometry, thus helping in much easier representation of complex shapes in an input signal as compared to conventional speech parameters. Furthermore, experimental results on the use of these short-term fractal components on pooling with Mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) have been recorded with modest changes using hidden Markov models (HMM). The selection of optimal features was made possible by increasing child data through adaptation measures on adult data, which has allowed for the examination of new features under mismatched conditions resulting in an overall improvement of 11.54% in the performance of the proposed ASR framework
Abstract: In this paper, the Punjabi children speech recognition system is developed using Subspace Gaussian mixture models (SGMM) acoustic modeling techniques. Initially, the system is dependent upon Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) approach for controlling the temporal variations in the input speech signals. Here, SGMM is integrated with HMM to measure the efficiency of each state which carries the information of a short-windowed frame. For handling the children speaker acoustic variations speaker adaptive training (SAT), based on vocal-tract length normalization and feature space maximum likelihood linear regression is adopted. Kaldi and open-source speech recognition toolkit is used to develop the Robust Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) System for Punjabi Children's speech. S GMM accumulate the frame coefficients and their posterior probabilities and pass these probabilities to HMM which systematically fit the frame and output have resulted from HMM states. Therefore, the achievement of SGMM has gotten a large performance margin in Punjabi children speech recognition. A remarkable depletion in the word error rate (WER) was noticed using SGMM by varying the feature dimensions. The developed children ASR system obtained a recognition accuracy of 83.66% while tested by varying the feature dimensions to 12.
Abstract: Despite significant progress has been made in building of ASR system for various adult speech, whereas the children ASR system is still in infant stage for Indian languages. To build Punjabi children speech recognition is one such challenge because of unavailability of zero-speech corpus. In this paper, efforts have been made to build small vocabulary Punjabi continuous children speech corpus. In explored system, four variations of bMMI discriminative techniques have been perform on two context models: Dependent and Independent. Experiment result have shown that system attains Relative Improvement (RI) of 22-26% on fbMMI and fMMI acoustic model as compared to other approaches. Various combination of parameter has been implemented with variation in boosted parameter and iteration values to obtain optimal value of bMMI and fbMMI acoustic models.
Abstract: Robustness of the automatic speech recognition (ASR) system relies upon the accuracy of feature extraction and classification in training phase. The mismatch between training and testing conditions during classification of large feature vectors causes a low performance. In this paper, the issue of robustness of acoustic information is addressed for practical Punjabi dataset. Traditional feature extraction approaches: mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) and gammatone frequency cepstral coefficients (GFCC) face the issue of high variance with leakage of spectral information. Also, handling of the huge number of feature information creates chaos for large speech vocabulary. To overcome this dilemma, a Principal component analysis (PCA) based multi-windowing technique is proposed with the incorporation of baseline GFCC and MFCC based feature approaches after the tuning of taper parameter. The proposed integrated approaches result in better feature vectors, which are further processed using differential evolution + hidden Markov model (DE + HMM) based modelling classifier. The integrated approaches show substantial performance for word recognition as compared to the conventional or fused feature extraction systems.
Abstract: A baseline ASR system does not perform better due to improper modeling of training data. Training of system through conventional HMM technique faced the issue of on or near manifold in data space. In this paper, Hybrid SGMM-HMM approach is compared with baseline GMM-HMM technique on Punjabi continuous simple sentences speech corpus. It examined the hybridized HMM technique: SGMM-HMM to overcome the problem of sharing of state parameter information throughout the training and testing of system. The system testing is performed on Kaldi 4.3.11 toolkit using MFCC and GFCC approaches at the front end of the system. The result obtained on SGMM-HMM modeling technique generates an improvement of 3–4% over GMM-HMM approach. The experiments are performed on real environment dataset.
Abstract: Dengue is a viral disease which affects public health every year in global wise. Every change in climate in a particular location increases the probability of spreading dengue disease in that domain. There are number of health schemes running by governments to prevent and control dengue disease at early stages. The usage of information technology helps to achieve this goal. There is a huge need to develop machines which enable medical technicians to detect dengue disease at early stages. For achieving this goal, the author efforts to detect dengue dataset which helpful to develop a machine learning prediction model for dengue disease. The author conducts analytical study by collecting symptoms and clinical tests conducting by researcher in the same domain. To detect important factors of dengue, the author uses the statistical and support machine. Here, author effort shows four important factors fever, headache, skin rash and abdominal pain used to detect dengue at early stage
Abstract: India is the land of language diversity with 22 major languages having more than 720 dialects, written in 13 different scripts. Out of 22, Hindi, Bengali, Punjabi is ranked 3rd, 7th and 10th most spoken languages around the globe. Expect Hindi, where one can find some significant research going on, other two major languages and other Indian languages have not fully developed Automatic Speech Recognition systems. The main aim of this paper is to provide a systematic survey of the existing literature related to automatic speech recognition (i.e. speech to text) for Indian languages. The survey analyses the possible opportunities, challenges, techniques, methods and to locate, appraise and synthesize the evidence from studies to provide empirical answers to the scientific questions. The survey was conducted based on the relevant research articles published from 2000 to 2018. The purpose of this systematic survey is to sum up the best available research on automatic speech recognition of Indian languages that is done by synthesizing the results of several studies.
Abstract: Image fusion acts as a powerful tool in the medical domain. It is an essential method for enhancing the quality of images by combining the complementary images which are captured from various sensors or cameras. The aim of multi modal image fusion technique is to obtain a single fused image by fusing the images of different modalities. It is widely used in various clinical applications for better diagnosis of several types of diseases. In this paper, comparative analysis has been made using various multi modal techniques in medical domain such as guided filter, multi resolution singular value decomposition and principal component analysis. The quantitative and qualitative results have been taken. The experiment results indicated that guided filter method is more efficient as compared to other methods in terms of evaluation metrics such as standard deviation is 29.8, mean is 52.3, entropy is 2.8 and fusion information score is 0.8. It has also been observed that guided filter is able to preserve edges efficiently and is more suitable for real applications.
Abstract: HMM is regarded as the leader from last five decades for handling the temporal variability in an input speech signal for building automatic speech recognition system. GMM became an integral part of HMM so as to measure the efficiency of each state that stores the information of a short windowed frame. In order to systematically fit the frame, it reserves the frame coefficients and connects their posterior probability over HMM state that acts as an output. In this paper, deep neural network (DNN) is tested against the GMM through utilization of many hidden layers which helps the DNN to successfully evade the issue of overfitting on large training dataset before its performance becomes worse. The implementation DNN with robust feature extraction approach has brought a high performance margin in Punjabi speech recognition system. For feature extraction, the baseline MFCC and GFCC approaches are integrated with cepstral mean and variance normalization. The dimension reduction, decorrelation of vector information and speaker variability is later addressed with linear discriminant analysis, maximum likelihood linear transformation, SAT, maximum likelihood linear regression adaptation models. Two hybrid classifiers investigate the conceived acoustic feature vectors: GMM–HMM, and DNN–HMM to obtain improvement in performance on connected and continuous Punjabi speech corpus. Experimental setup shows a notable improvement of 4–5% and 1–3% (in connected and continuous datasets respectively).
Abstract: Punjabi is tonal as well as under resource language among all the Indo Aryan languages of the Indo-European family. A vast number of variations in language lead to challenges while designing an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system. Therefore, it turned out to be a matter of extreme concern to study the essential features such as tone of the language for designing an effective ASR. This paper lays its focus upon the variation of tonal characteristics of Punjabi dialect. The speech corpus has been collected from native speakers of Punjab (including all the various dialects) and also covering the areas under the Himachali belt of Punjab. The result analysis shows that tonal words and dialectal word information caste a major impact on the information conveyed by the speaker. The analyzed data shows pitch variations in tonal words that vary from region to region. The experiments are performed by using Praat toolkit for calculating F0 value; then depending upon the pitch and frequency variations, we have studied that tonal words show dialectal variations when the similar sentence is spoken by speakers of different regions.
Abstract: Punjabi language has almost 105 million native speakers and faced the challenge of less resource. The Punjabi ASR system has little research as compared to other Indian languages. This paper examines the continuous vocabulary of Punjabi language using Sphinx toolkit. The proposed work has been implemented on speaker-independent and speaker-dependent speakers in different environmental conditions. The Punjabi ASR system has been trained on 442 phonetically rich sentences using 15 speakers (6 Male and 9 female). The system adopts MFCC at the front end and HMM at the modelling phase to extract and classify feature vectors. The simulation result demonstrates the performance improvement of 93.85% on speaker-dependent dataset and 89.96% on speaker-independent dataset.
Abstract: An automatic speech recognition system follows an approach of pattern matching, which consists of a training phase and testing phase. Despite advancement in training phase, the performance of the acoustic model is adverse while adopting the statistical technique like hidden Markov model (HMM). However, HMM-based speech system faces high computational complexity and becomes challenging to provide accuracy during isolated Punjabi lexicon. As the corpus of the system increases, the complexity of training phase will also increase drastically. The redundancy and confusion occurred between feature distributions in training phase of the system. This paper proposes an approach for the generation of HMM parameters using two hybrid classifiers such as GA+HMM and DE+HMM. The proposed technique focuses on refinement of processed feature vectors after calculating its mean and variance. The refined parameters are further employed in the generation of HMM parameters that help in reduction of training complexity of the system. The proposed techniques are compared with an existing technique such as HMM on benchmark databases and self-developed corpus in clean, noisy, and real-time environments. The results show the performance improvement in pattern matching of spoken utterance when demonstrated on large vocabulary isolated Punjabi lexicons.
Abstract: Automatic speech recognition (ASR) system plays a vital role in the human–machine interaction. ASR system faces the challenge of performance degradation due to inconsistency between training and testing phases. This occurs due to extraction and representation of erroneous, redundant feature vectors. This paper proposes three different combinations at speech feature vector generation phase and two hybrid classifiers at modeling phase. In feature extraction phase MFCC, RASTA-PLP, and PLP are combined in different ways. In modeling phase, the mean and variance are calculated to generate the inter and intra class feature vectors. These feature vectors are further adopted by optimization algorithm to generate refined feature vectors with traditional statistical technique. This approach uses GA + HMM and DE + HMM techniques to produce refine model parameters. The experiments are conducted on datasets of large vocabulary isolated Punjabi lexicons. The simulation result shows the performance improvement using MFCC and DE + HMM technique when compared with RASTA-PLP, PLP using hybrid HMM classifiers.
Abstract: Speech to text conversion in various languages have been performed so far but no process has defined for the Kashmiri language. There has been no research done on Kashmiri speech recognition. So in this work, we describe the development as well as implementation of first CMU Sphinx-3 based speech recognizer for the Kashmiri language. Recognition of the words have been done by using hidden markov models (HMMs). Dictionary consists of 100 words, representing Kashmiri digits from one (akh) to hundred (hat). Here, we developed a speaker independent, Kashmiri - Automatic Speech Recognition (KASR) system. The System is trained and tested for 1200 words spoken by 12 male and female speakers. Maximum Accuracy of 78.33% was achieved by the K-ASR system.
Abstract: A Hindi dialect (Bangro) Spoken Language Recognition (HD-SLR) System is designed to recognize language from a given spoken utterance. Paper focuses on the influence of Hindi dialects, i.e., Haryanvi spoken by males and females of different age groups ranging from 18 to 40 years. The system is trained and tested with the help of Sphinx3 toolkit on Linux platform. Also, it has been tried with semicontinuous speech corpus in clean environment of around 5 h that includes 1000 distinct Hindi dialect words spoken in different parts of Haryana. The dialectal information of the input speech signals is extracted with the help of MFCC technique and the same system is then tested on the basis of utterance level. The Speaker Independent Semicontinuous (SISC) word recognition system has an average of 75–85 % accuracy rate by native and nonnative speakers of Hindi dialect.
Abstract: Natural language and human–machine interaction is a very much traversed as well as challenging research domain. However, the main objective is of getting the system that can communicate in well-organized manner with the human, regardless of operational environment. In this paper a systematic survey on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for tonal languages spoken around the globe is carried out. The tonal languages of Asian, Indo-European and African continents are reviewed but the tonal languages of American and Austral-Asian are not reviewed. The most important part of this paper is to present the work done in the previous years on the ASR of Asian continent tonal languages like Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, Mandarin, Mizo, Bodo and Indo-European continent tonal languages like Punjabi, Lithuanian, Swedish, Croatian and African continent tonal languages like Yoruba and Hausa. Finally, the synthesis analysis is explored based on the findings. Many issues and challenges related with tonal languages are discussed. It is observed that the lot of work have been done for the Asian continent tonal languages i.e. Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, Mandarin but little work been reported for the Mizo, Bodo, Indo-European tonal languages like Punjabi, Latvian, Lithuanian as well for the African continental tonal languages i.e. Hausa and Yourba.
Abstract: In modern speech recognition systems, there are a set of Feature Extraction Techniques (FET) like Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) or perceptual linear prediction coefficients (PLP) are mainly used. As compared to the conventional FET like LPCC etc, these approaches are provide a better speech signal that contains the relevant information of the speech signal uttered by the speaker during training and testing of the Speech To Text Detection System (STTDS) for different Indian languages. In this dissertation, variation in the parameters values of FET’s like MFCC, PLP are varied at the front end along with dynamic HMM topology at the back end and then the speech signals produce by these techniques are analyzed using HTK toolkit. The cornerstone of all the current state-of-the-art STTDS is the use of HMM acoustic models. In our work the effectiveness of proposed FET(MFCC, PLP features) are tested and the comparison is done among the FET like MFCC and PLP acoustic features to extract the relevant information about what is being spoken from the audio signal and experimental results are computed with varying HMM topology at the back end.
Abstract: This paper frames correlation on three feature extraction techniques in ASR system. As compared to primarily used technique called MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients), PNCC (Power Normalized Cepstral Coefficients) obtains impressive advancement in noisy speech recognition due of its inhibition in high frequency spectrum for human voice. The techniques differ in the way as MFCC uses traditional log nonlinearity and PNCC processing substitute the usage of power-law nonlinearity. Experimental results relay on the fact that PNCC processing provides substantial improvements in recognition accuracy compared to MFCC as well as PLP (Perceptual Linear Prediction) processing for speech recognition in the existence of various types of additive noise and reverberant environments with marginally greater computational cost and the with the usage of clean speech, it does not lowers the decoding accuracy.
Abstract: Green computing refers to the process of improving the efficiency of computing devices and reducing its negative impact on mankind and environment. Over the years the idea of green computing has attracted the world due to its environment benefits. At present green computing is under the consideration of businesses organizations and IT industries to improve environmental conditions for the better living of human being. It is an effective approach to protect our environment from the harmful effects of toxic material used during the manufacturing of computing devices. This paper is an attempt to discuss the need of green computing and the steps required to be taken to improve the environmental condition in current
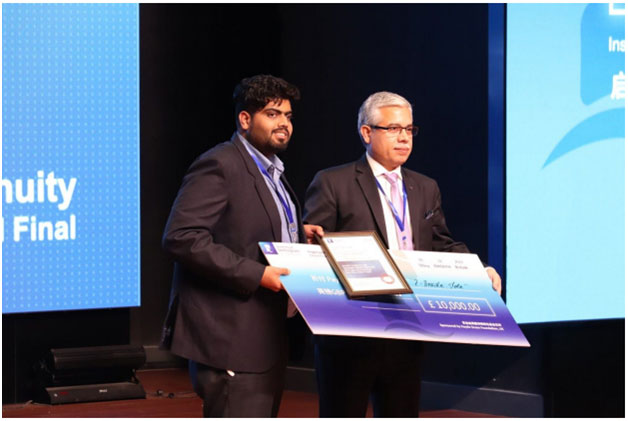
era.Winner of ‘Most International Project’ in University Of Nottingham, China at Global Ingenuity’18 Finals |
 |
|---|---|
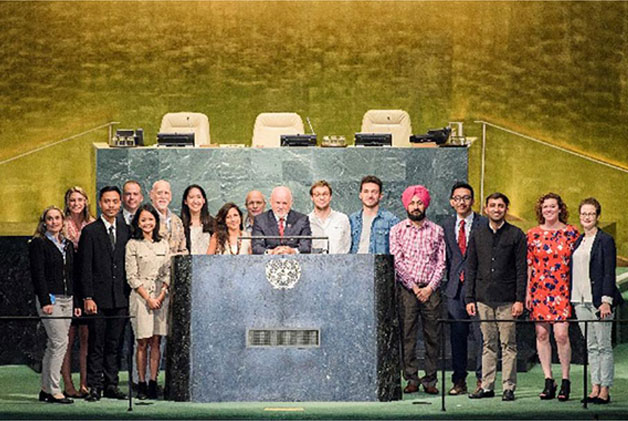
Dr. Virender Kadyan Wins 1st Prize and is Invited to United Nations Headquarters |
 |
Winner at ACM India Chapter Technology Solutions Contest 2019 |
 |
'Winner' at the Novate+ Himachal Pradesh winning grant of ₹2,50,00 |
 |
Winner of Punjab Innovation Summit 2019 |
 |
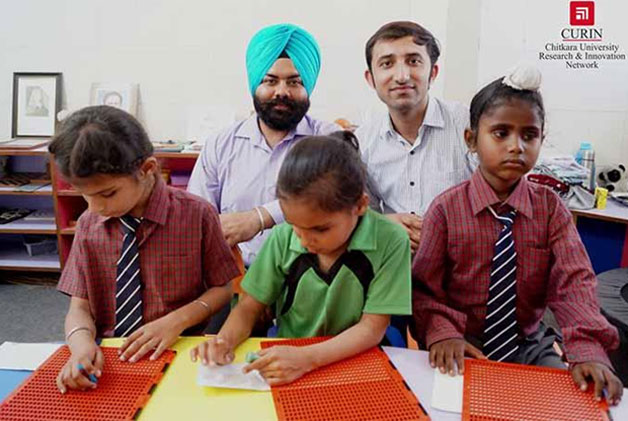
Speech Lab members presented BrilTab Edukit-1 and Child-Ensign project at UN House, Delhi on 7 Sept 2019 |
 |
Winner of HACKTIET’19, A 24-Hour Hackathon Organised By DSC, Thapar And GirlScript, Patiala |
 |
Winner of Chitkara Master Code Chef - Season 3 (Code Hackathon) |
 |
Winners Of UN Influx-Global Hackathon 2017 |
 |